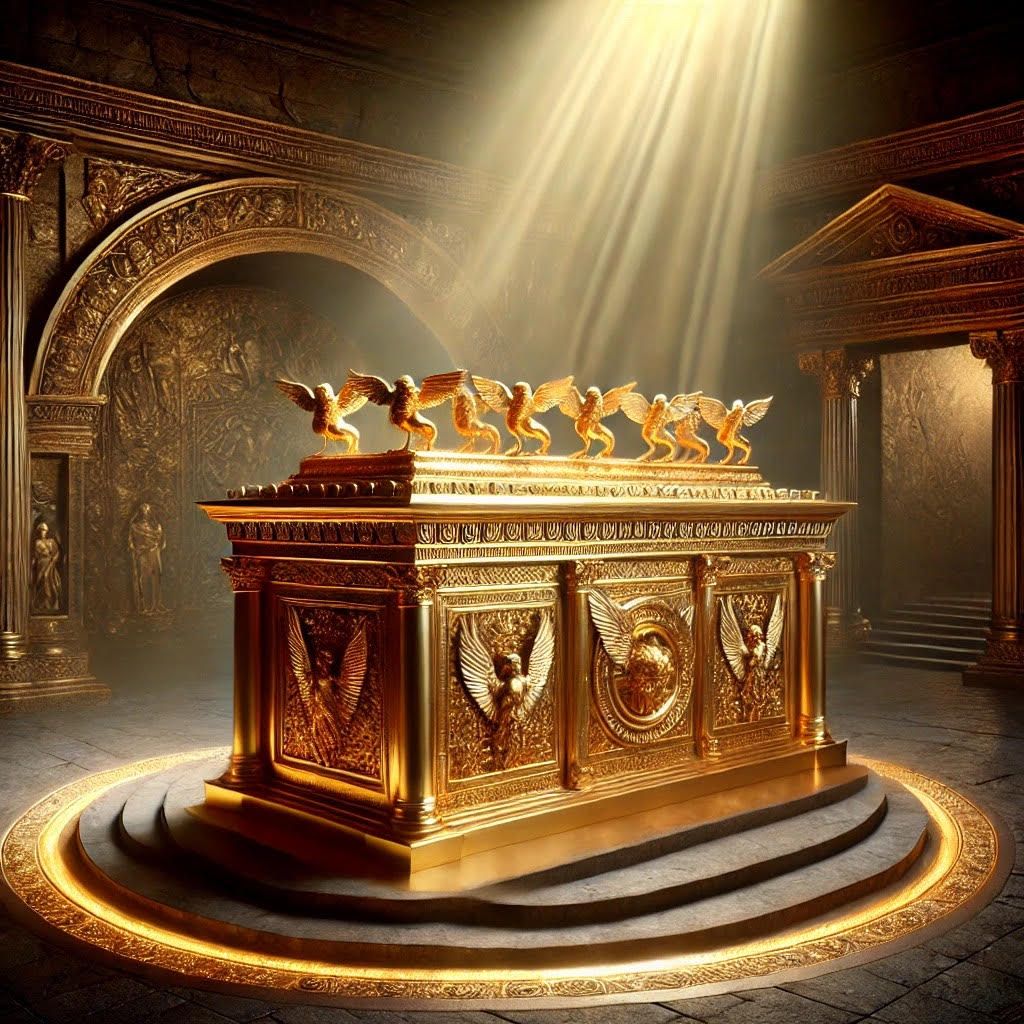

The Ark of the Covenant is one of the most intriguing and mysterious artifacts in human history. Mentioned extensively in the Bible, it is said to have held the stone tablets of the Ten Commandments and symbolized God’s covenant with the Israelites. Its disappearance has fueled centuries of speculation, inspiring religious devotion, archaeological quests, and even pop culture references.
This blog delves into the Ark’s historical significance, its mysterious disappearance, modern research efforts, and the critical role Ethiopia plays in preserving the legacy of the Christian faith.

What Is the Ark of the Covenant?
The Ark of the Covenant was a sacred chest, built by the Israelites under divine instruction (Exodus 25:10-22). It was made of acacia wood, overlaid with gold, and adorned with two cherubim on its lid, known as the “Mercy Seat.”
Significance of the Ark
1. Symbol of Divine Presence: The Ark represented God’s tangible presence among the Israelites. It was carried during their journey through the wilderness and into battles as a source of protection and divine guidance.
2. Container of Sacred Relics: The Ark held the stone tablets of the Ten Commandments, a golden jar of manna, and Aaron’s rod that budded (Hebrews 9:4).
3. Worship and Ritual: Housed in the Holy of Holies within the Tabernacle (and later Solomon’s Temple), it was central to Jewish worship. Only the high priest could approach it, and then only on Yom Kippur, the Day of Atonement.
The Mystery of the Ark’s Disappearance
The Ark vanished from historical records around the time of the Babylonian conquest of Jerusalem in 586 BCE. Its fate remains unknown, giving rise to numerous theories about its location and status.

Theories on the Ark’s Whereabouts
1. Hidden in Jerusalem: Some believe the Ark was hidden beneath the Temple Mount to protect it from invaders.
2. Transported to Ethiopia: Ethiopian tradition claims the Ark resides in Axum, in the Church of Our Lady Mary of Zion, guarded by a single monk who dedicates his life to its protection.
3. Lost or Destroyed: Some scholars speculate the Ark was destroyed during the Babylonian invasion or lost over time.
4. Knights Templar Connection: Medieval legends suggest the Knights Templar found the Ark during the Crusades and transported it to Europe, but no evidence supports this claim.
Scientific and Historical Research on the Ark
While the Ark is primarily a religious artifact, it has drawn significant interest from archaeologists, historians, and scientists. Key research and investigations include:
1. Excavations in Jerusalem
• Archaeologists have conducted extensive digs around the Temple Mount, but access is limited due to its religious and political sensitivity. No direct evidence of the Ark has been found.
2. Mount Nebo Theories
• Some researchers believe the Ark could be hidden in Mount Nebo (modern-day Jordan), based on a reference in 2 Maccabees 2:4-8, which suggests that the prophet Jeremiah hid it there.
3. Ethiopian Claims
• The Ethiopian Orthodox Church has steadfastly maintained that the Ark resides in Axum. Scholars like Edward Ullendorff have investigated these claims, but no definitive proof has emerged. The church prohibits external examination of the artifact, further deepening the mystery.
4. Documentary and Forensic Investigations
• Various documentaries have attempted to trace the Ark’s journey, exploring theories from Africa to the Middle East. These efforts, while fascinating, remain speculative.
Ethiopia: A Keeper of Christian Faith
Ethiopia holds a unique position in Christian history and tradition. One of the oldest Christian nations in the world, Ethiopia adopted Christianity in the 4th century under King Ezana. The Ethiopian Orthodox Church is central to this legacy, preserving ancient Christian traditions and artifacts, including claims to the Ark of the Covenant.

Significance of Ethiopia’s Christian Heritage
1. Axum and the Ark
• The city of Axum is a spiritual center for Ethiopian Christianity. The Church of Our Lady Mary of Zion is believed to house the Ark, underscoring Ethiopia’s role as a guardian of biblical tradition.
2. The Ethiopian Bible
• The Ethiopian Orthodox Church preserves one of the oldest and most complete biblical canons, including books not found in other Christian traditions.
3. Monastic Traditions
• Ethiopia’s monasteries, often in remote and rugged locations, have been vital in safeguarding Christian texts and traditions through centuries of external threats.
4. Connection to Early Christianity
• Ethiopia is mentioned in the Bible (e.g., Acts 8:26-40, the story of the Ethiopian eunuch), highlighting its early connection to the Christian faith.
Ethiopia’s steadfast devotion to its faith, even in the face of invasions and isolation, has cemented its role as a cornerstone of Christianity in Africa and the world.
Conclusion
The Ark of the Covenant remains one of history’s greatest mysteries. Its spiritual significance, coupled with its disappearance, has inspired countless theories and investigations. While no definitive evidence of its location has been found, Ethiopia stands out as a beacon of faith and tradition, preserving the story of the Ark and its connection to Christian heritage.
Whether hidden beneath Jerusalem, resting on Mount Nebo, or safeguarded in Axum, the Ark’s legacy continues to inspire awe and devotion. As a symbol of divine presence and covenant, it challenges us to reflect on the enduring power of faith and the mysteries of the past.
References and Further Reading
1. The Bible: Exodus 25, 2 Samuel 6, 1 Kings 8.
2. Edward Ullendorff, The Ethiopians: An Introduction to Country and People.
3. Tudor Parfitt, The Lost Ark of the Covenant: Solving the 2,500-Year-Old Mystery of the Fabled Biblical Ark.
4. Graham Hancock, The Sign and the Seal: The Quest for the Lost Ark of the Covenant.
5. Archaeological reports from the Israel Antiquities Authority and Mount Nebo excavations.
6. Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church resources on the Ark and Axum.
Ethiopia’s role as a guardian of faith ensures that the mystery of the Ark, whether tangible or symbolic, remains alive for future generations.
I want to thank you for being part of this community. If you’re in the mood for some shopping, be sure to check out the Amazon affiliate links attached to this blog. From top-rated home essentials to self-care favorites, you find something perfect for the season. (As an Amazon Associate, I earn from qualifying purchases.)





One thought on “Ethiopia and the Ark of the Covenant: A Sacred Legacy”